Watch on YouTube - Video notes - Video sections playlist - MES Science playlist
In this video, I provide a detailed look at cellular respiration, the set of metabolic reactions and processes in cells that convert chemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is considered the 'energy currency of the cell.' When oxygen is not present, fermentation can occur, resulting in waste products like lactic acid (in animals) or ethanol (in yeast and plants). Cellular respiration involves transporting electrons through an electron transport chain until the final acceptor, which is molecular oxygen. Anaerobic respiration, which uses electron acceptors other than molecular oxygen, should not be confused with fermentation.
Timestamps:
Cellular respiration converts chemical energy into adenosine triphosphate (ATP): 0:00
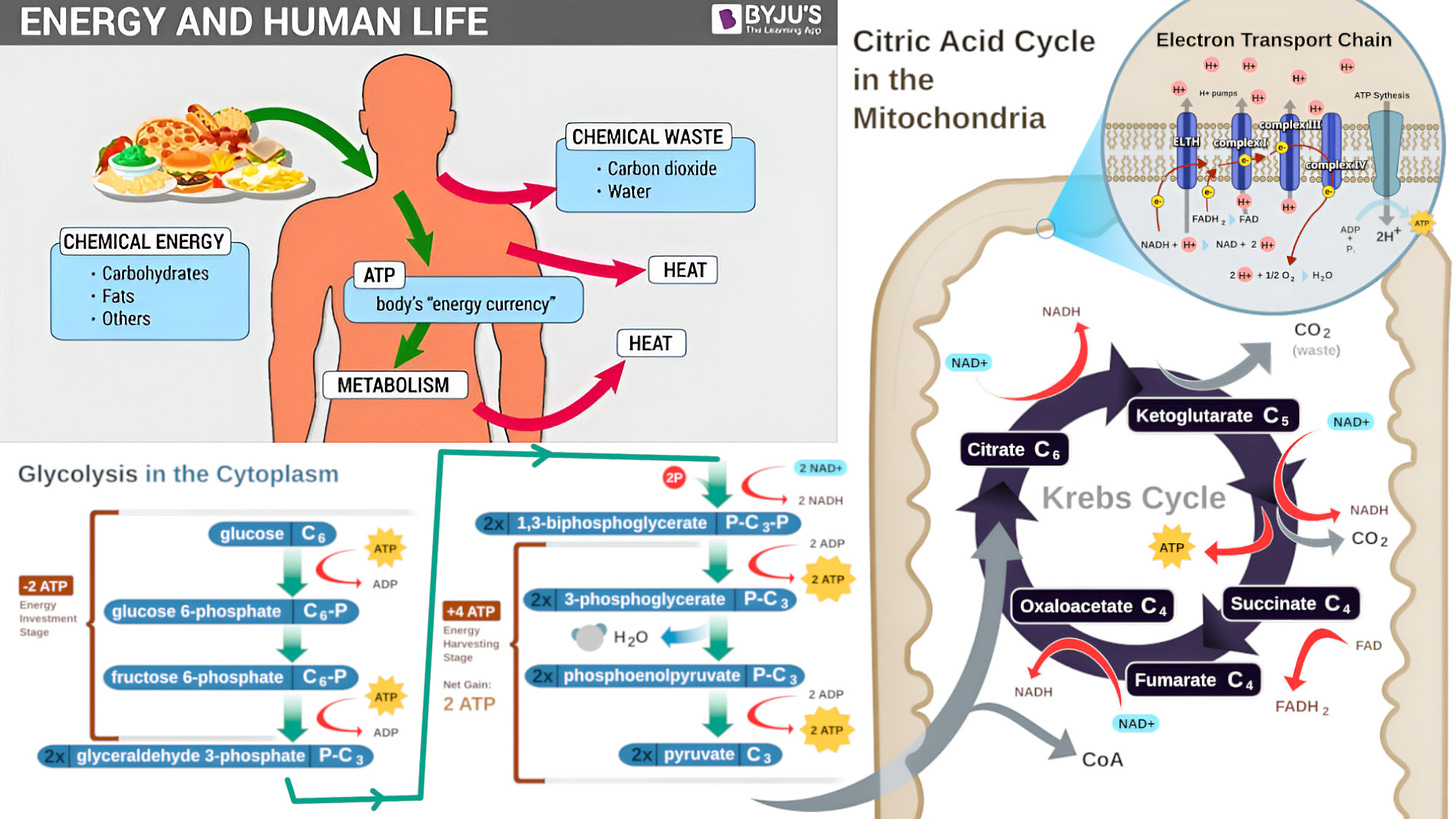
Energy and human life diagram: Slow motion combustion reaction: 1:49
Respiration in a eukaryotic cell: Glycolysis and Citric Acid Cycle: 2:40
Sugar in the form of glucose is the main nutrient involved in respiration: 3:45
Glycolysis in converts glucose into two pyruvates and ATP: 4:36
Formal charge assumes covalent bonds share charge equally regardless of relative electronegativity: 10:48
Electron shell may be thought of as an orbit of electrons around an atom's nucleus: 16:21
Atomic orbitals wave functions of the electron in a Hydrogen atom: 24:02
Vitamin are essential nutrients needed in small quantities for proper functioning during metabolism: 32:13
Citric Acid Cycle (CAC) releases stored energy through oxidation of acetyl-CoA from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins: 37:07
Oxidative phosphorylation use enzymes to oxidize nutrients to release chemical energy to produce ATP: 44:39
Electron transfer terminates with molecular oxygen as the final electron acceptor: 58:46 - If oxygen were not present, pyruvate would undergo fermentation instead of cellular respiration: 59:12
Post-Glycolysis processes: 1:01:01 - Respiration vs Fermentation chart: 1:04:29
Lactic acid fermentation: 1:05:16
Ethanol fermentation: 1:09:34
Substrate-level phosphorylation: Converts ADP directly to ATP: 1:10:55
Gluconeogenesis (GNG): Generates glucose from non-carbohydrate carbon substrates: 1:15:00
Ethanol fermentation chart: 1:18:06
Anaerobic respiration uses electron acceptors other than molecular oxygen: 1:21:02



















Cellular Respiration: Glycolysis, Citric Acid Cycle, Lactic Acid Fermentation, Anaerobic Respiration