YouTube - Notes - Full video and playlist - MES Science playlist
In this video I discuss the wide variety of plants, which are mainly eukaryotes that obtain energy from the Sun via photosynthesis. There are over 410,000 known species of land plants and about 391,000 of them are vascular plants, which have xylem and phloem to conduct water, minerals, and photosynthetic products. 369,000 species of the vascular plants are flowering plants, and 20,000 are bryophytes. Flowering plants, or angiosperms, produce fruits that contain the seeds, which are produced via pollination. Gymnosperms (Greek for "naked seeds"), such as pine trees, develop seeds directly on the surface of their scales or leaves, rather than in fruits.
Timestamps:
Plants are mainly multicellular and photosynthetic eukaryotes: 0:00
Vascular plants have over 300,000 known species and have lignified tissues (xylem) for conducting water and minerals, and non-lignified tissues (phloem) for conducting products of photosynthesis: 1:21
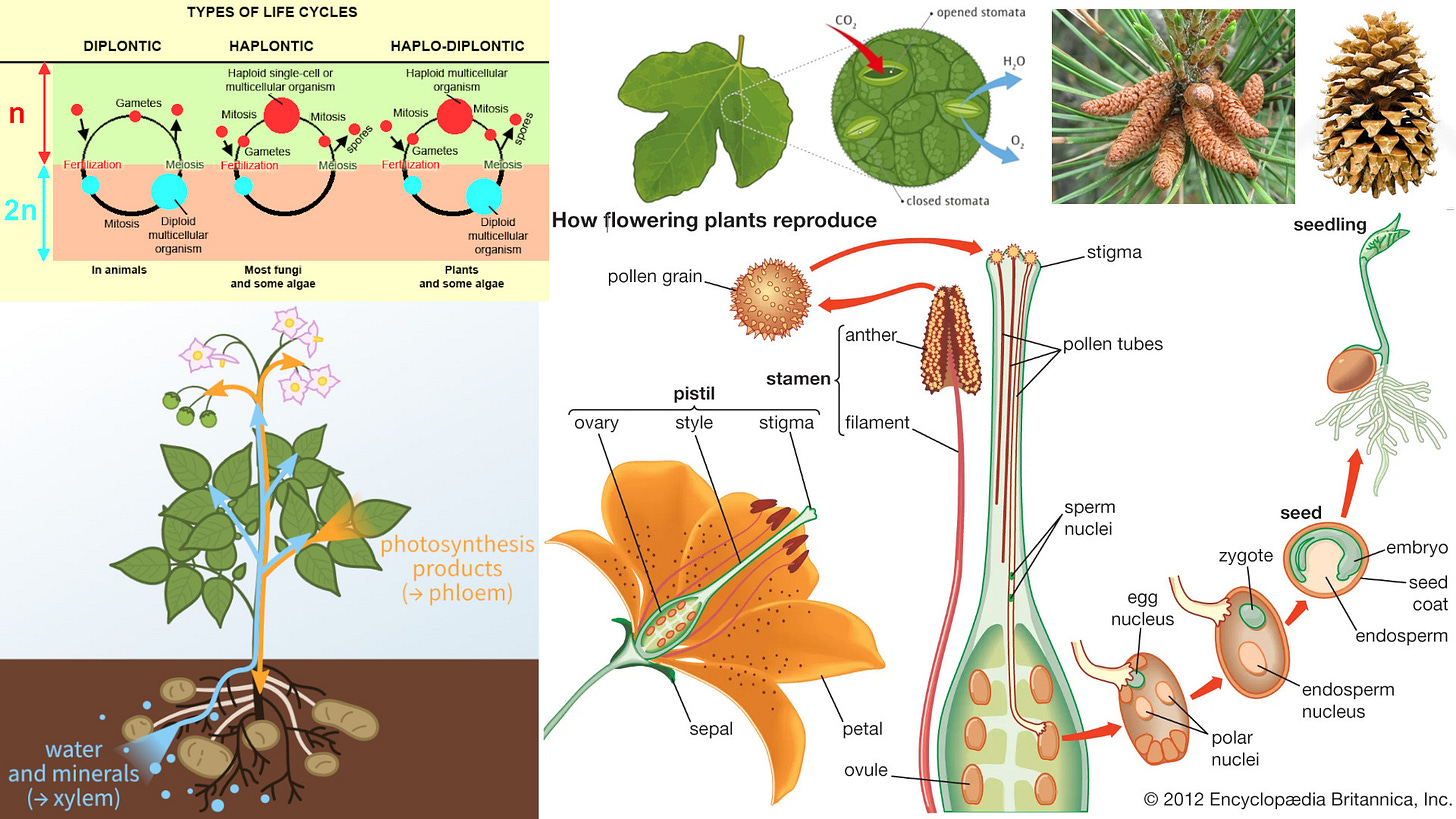
Xylem and phloem diagram: 3:17
Types of wood comparison: 7:07
Flowering plants (angiospermae) are seed-producing, have flowers, and produce fruits that contain the seeds: 7:25
Flowering plants reproduce by transferring pollen from anther to stigma of another flower: 10:09
Self-pollination vs cross-pollination diagram: 14:29
Bryophytes are the non-vascular and non-flowering land plants: liverworts, hornworts, and mosses: 16:12
Biological life cycle: 18:02
Haplontic life cycle: haploid stage is multicellular and diploid stage is a single cell: 20:52
Diplontic life cycle: diploid stage is multicellular and haploid gametes are formed: 21:13
Haplodiplontic life cycle: multicellular diploid and haploid stages occur: 21:59
Haplontic, Diplontic, and Haplo-diplontic life cycles and their timings of mitoses: 25:20
Types of life cycles diagram: 29:13
Alternation of generations are haplo-diplontic and alternate between multicellular diploid and haploid stages: 32:44
Diagram of alternation of generations between diploid sporophyte and haploid gametophyte: 39:22
Pollen grains are male microgametophytes of seed plants and produce male gametes (sperm cells): 41:34
Angiosperms (flowering plants) have the megagametophyte being only a few nuclei and cells: 44:55
Liverwort, Hornwort, and Moss images: 46:29
Diversity of plants images: 47:08
Algae is a large and diverse group photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms: 47:32
Comparison of algae and plants: 49:24
Autotrophs are primary producers and produce complex compounds using carbon from simple substances such as CO2 and usually using energy from light (photosynthesis) or inorganic chemical reactions (chemosynthesis): 54:04
Diagram of autotrophs and heterotrophs: 55:18
Microalgae are not visible to the naked eye: 57:03
Magnified leaf stomate showing opening for gas exchange: 58:32
Nonvascular plants don't have xylem or phloem, and rely on simpler tissues for internal water transport: 59:25
Seed plants comprise 5 divisions, 4 of which are gymnosperms and one is angiosperms: 1:00:25
Female pine cones in upper branches open up and receive pollen from the male pine cones in the lower branches: 1:03:41
Comparison between gymnosperm seeds and angiosperm seeds (in fruits): 1:05:22 - Gymnosperm seeds are naked: 1:06:22
Male pine or pollen cones image: 1:07:37
Angiosperms are most diverse group of land plants: 1:09:22













Share this post