YouTube - Summary - Notes - Playlist - MES Science playlist
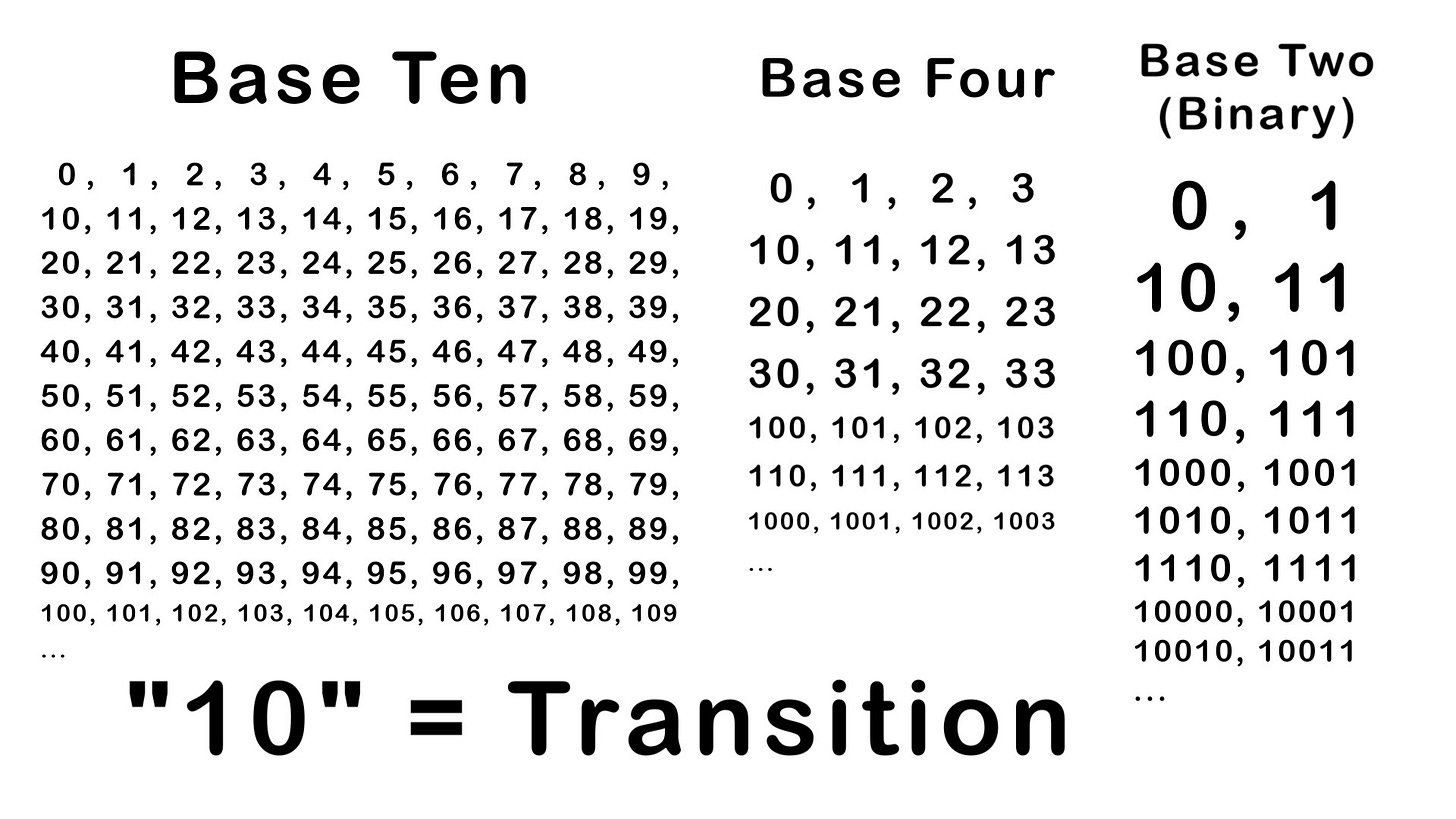
In this video I go over a quick overview of number systems, and show how the base or radix (Latin for “root”) serves as the transition point when counting past the single digits. For example, in the base ten number system: the single digits are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and then the transition is 9 + 1 = 10. Then the cycle repeats again to 11, 12, 13, etc., until the transition becomes 20.
For the base four number system, the single digits are 0, 1, 2, 3 and then the transition is 3 + 1 = 10, and the cycle repeats 11, 12, 13, 20, 21, etc.
For the base two or binary number system, the single digits are just 0 & 1, and then the transition is 1 + 1 = 10, and the cycle repeats 11, 100, 101, 110, 111, 1000, 1001, etc.
Thus even though “10” is associated with the most common base ten number system, keep in mind that it is merely a transition number, and that the number “ten” is different using different number systems. Stay tuned for my next video in which I show how to convert between number systems!
#math #radix #education #numbertheory #arithmetic
Timestamps
Overview of Base Number Systems – 0:00
The number 10 (radix (root) or base) in general number systems – 0:11
Base 10 (Ten): 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9. The 10 = 9 + 1, and is the transition indicator – 0:50
Example 1: Base 4 (Four): 0, 1, 2, 3. The 10 = 3 + 1, and is the transition indicator – 3:55
Example 2: Binary or Base 2 (Two): 0, 1. The 10 = 1 + 1, and is the transition indicator – 6:05